Tsunamis generated by granular collapse
Members: I. Le Pivert--Jolivet, A. Kane, C. Morize, and P. Gondret
Collaborations: A. Sauret (UCSB).
Former members: W. Sarlin, M. Robbe-Saule, Y. Bertho, A. Hildenbrand (GEOPS), R. Henaff.
Although many tsunamis arise from tectonic events, various past situations showed that sudden
large landslides can also lead to devastative events. In order to estimate the hazards induced by these
tsunamis on coastlines we investigate this situation through model laboratory experiments. The experiments consists of the collapse of an initially dry column of grains into a shallow water layer
and the subsequent generation of waves.
The experiments show that the collective entry of the granular material into water governs the wave generation process. The wave amplitude relative to the water depth is indeed driven by the Froude number based on the horizontal velocity of the moving granular front relative to the wave velocity. Three nonlinear wave regimes has been identified depending on the Froude number: transient bores for large Fr, solitary-like waves for intermediate value of the Froude number and nonlinear transition waves at small Fr. We showed that the wave amplitude and the wavelength, relative to the water depth, exhibit nonlinear scalings with the Froude number.

Fig. 1: Bore wave generated by the collapse of a granular column at Fr=1.4.

Fig. 2: Solitary-like wave generated at Fr=0.7.

Fig. 3: Nonlinear transition wave generated at Fr=0.2.
Moreover, we showed that the maximal amplitude reached near-shore by the generated wave in our experiments is linked to the instantaneous immersed volume of grains and to the ultimate immersed deposit. Despite the differences in scale and geometry between our small-scale experiments and larger-scale geophysical events, a rather good agreement is observed between the experimental law and the field data.
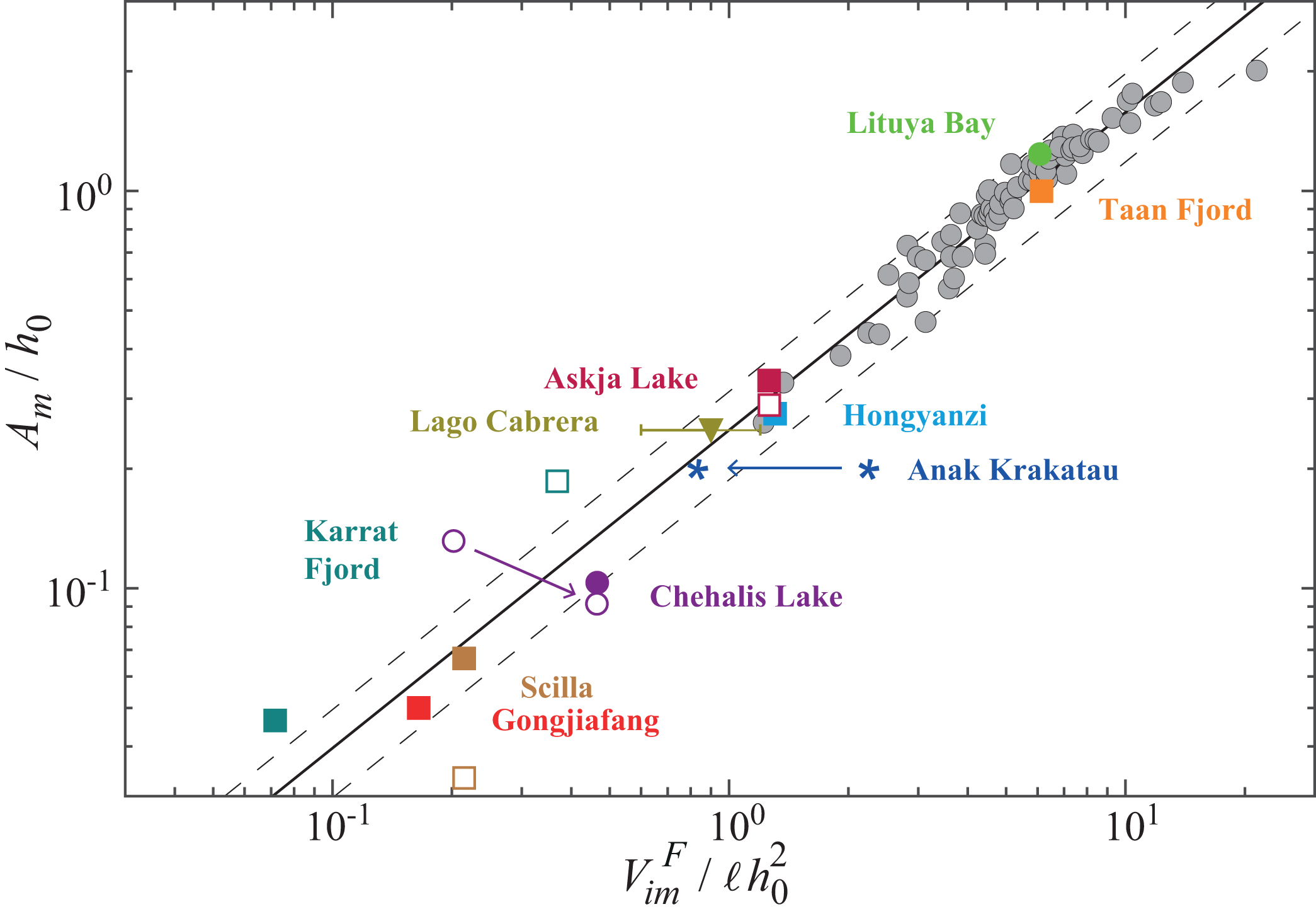
Fig. 4: Rescaled maximal amplitude of the wave generated near-shore as a function of the rescaled volume of the final immersed deposit for our experimental data (gray symbols) and data from the literature corresponding to historical cases of tsunamis generated by subaerial landslides (color symbols).
Publications
From granular collapses to shallow water waves: A predictive model for tsunami generation
W. Sarlin, C. Morize, A. Sauret, P. Gondret, Phys. Rev. Fluids 7, 094801 (2022).
Editor's suggestion and Featured in Physic's
[Abstract | PDF| suppl. material]
From laboratory experiments to geophysical tsunamis generated by subaerial landslides
M. Robbe-Saule, C. Morize, Y. Bertho, A. Sauret, A. Hildenbrand, P. Gondret, Sci. Rep. 11, 18437 (2021).
[Abstract | PDF | suppl. material]
Nonlinear regimes of tsunami waves generated by a granular collapse
W. Sarlin, C. Morize, A. Sauret, P. Gondret, J. Fluid Mech. 919, R6 (2021).
[Abstract | PDF | suppl. material | Cover]
Experimental investigation of tsunami waves generated by granular collapse into water
M. Robbe-Saule, C. Morize, R. Henaff, Y. Bertho, A. Sauret, P. Gondret, J. Fluid Mech. 907, A11 (2020).
[Abstract | PDF]
General public
Effondrement de chateaux de sable dans l'eau : des tsunamis de laboratoire
W. Sarlin, C. Morize, A. Sauret, P. Gondret, Reflets de la Physique 78 24-27 (2024).
[Abstract | PDF]
Highlights
Des billes tombant dans l eau predisent les tsunamis
Le Monde (05/10/2022).
[HTML]
Modeling Landslide-Induced Tsunamis
Physics (13/09/2022).
[HTML]
Tsunamis generes par effondrements de terrain : du modele au reel
Actualites scientifiques de l'Universite Paris-Saclay (16/12/2021).
[HTML]
Les tsunamis d'effondrement caracterises en laboratoire
Pour la Science 529, 27, October 2021.
[HTML]
Predire la generation de vagues de tsunamis causees par effondrement de terrain
Actualites Scientifiques de l'INSU-CNRS (19/10/2021).
[HTML]
The Science of Tsunamis
News UCSB (08/06/2021).
[HTML]
Des tsunamis generes a l'echelle du laboratoire
Actualites Scientifiques de l'INSIS-CNRS (01/02/2021).
[HTML]
|






